DO I HAVE HYPOTHYROIDISM?
- BY DR. AK RANA
Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism are two types of thyroid disorders.
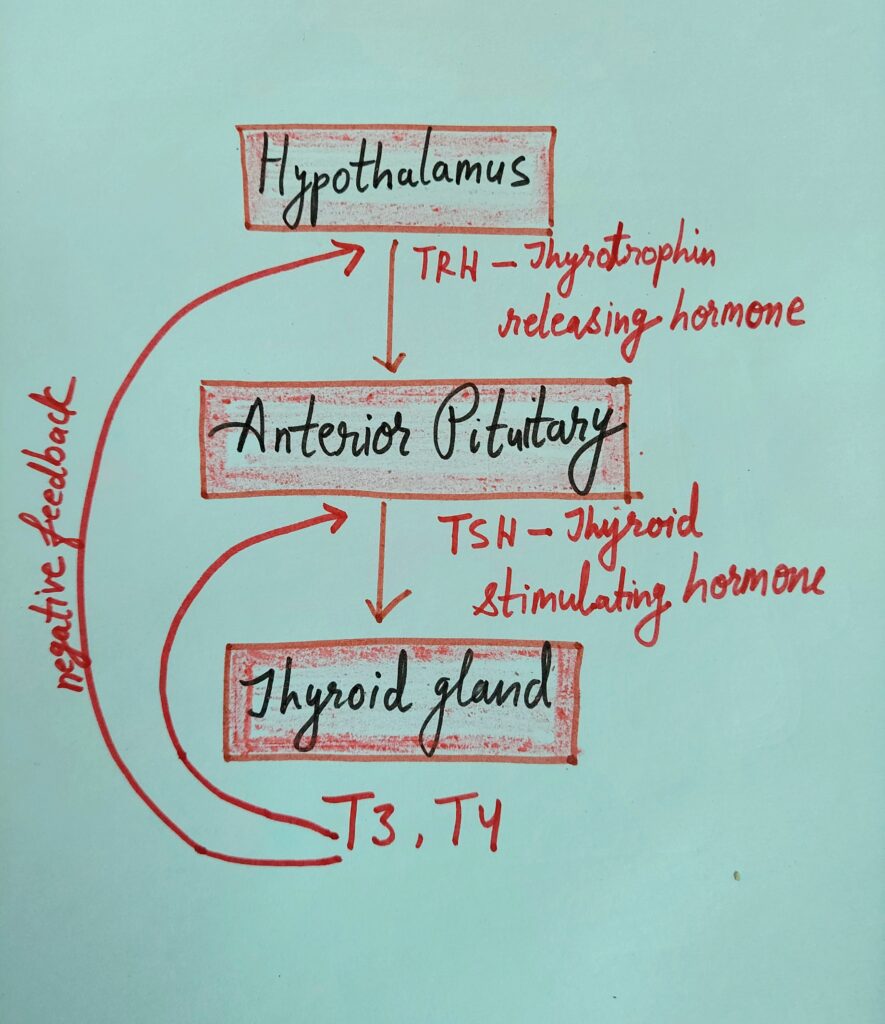
Thyroid gland releases thyroid hormones after getting stimulus from TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) released by pituitary gland.
TSH acts on the receptors present on thyroid gland and causes release of thyroid hormone.
There can be two cases –
- Increase in thyroid hormone called as Hyperthyroidism.
All the functions of thyroid hormone is increased.
- Decrease in thyroid hormone called as Hypothyroidism.
All the functions of thyroid hormone is decreased.
HYPOTHYROIDISM
- Thyroid hormone is involved in Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) of body.
In Hypothyroidism there is decrease in BMR.
- Thyroid hormone increase glucose production by glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
In hypothyroidism – Hypoglycemia is an important finding ( especially in myxedema coma ).
- Thyroid hormone promotes lipolysis (breakdown of lipids).
- Thyroid hormone is involved in cholesterol clearance. In its deficiency hypercholesterolemia takes place.
REGULATION OF THYROID HORMONE
HYPOTHYROIDISM IS OF TWO TYPES –
CONGENITAL – Present since birth.
ACQUIRED – It is further of two types-
Primary Hypothyroidism
Secondary Hypothyroidism
Primary Hypothyroidism – It is defect or problem which lies in thyroid gland, which is resulting in decreased release of thyroid hormone in body.
Secondary Hypothyroidism – Defect lies at central level, in either Hypothalamus or Pituitary gland.
Hypothalamus releases TRH (Thyrotropin releasing hormone) that acts on pituitary which further releases TSH that act on thyroid gland.
DIAGNOSIS
When you go to clinic for TFT (Thyroid function test).
They check two things usually-
- T3 and T4 ( forms of thyroid hormone)
- TSH
If it is Primary hypothyroidism then T3 and T4 will be decreased. It sends signal to pituitary to increase TSH.
Finally we will see decreased T3 and T4 while increased TSH.
If it is secondary hypothyroidism then T3 and T4 will be low because decreased TSH is released by Pituitary.
We will therefore see decreased T3 and T4 and also decreased TSH.
CAUSES OF HYPOTHYROIDISM
PRIMARY HYPOTHYROIDISM
- · Hashimoto thyroiditis
- · Iodine deficiency (endemic goiter)
- · Post surgery
- · Drugs blocking synthesis or release of T4 (for example – Lithium, sulfonamides)
- · Thyroiditis
SECONDARY HYPOTHYROIDISM
Any mass lesion in the brain which compresses the stalk eg. Lymphocytic hypophysitis
RISK FACTORS OF HYPOTHYROIDISM
- · Autoimmune disorder may be linked with similar family history.
- · Living in iodine deficient areas which causes enlargement of thyroid gland in order to meet the demand called goiter. Example – in hilly areas.
- · Goitrogenic food as the main diet like Broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower. Lacking balanced diet.
- · Thyroiditis – It is inflammation of thyroid gland.
Subacute thyoiditis / DeQuervain’s thyroiditis
It is generally seen in females of age group 30 – 50 years. In it firstly phase of toxicosis occurs with increased T3 ,T4 and decreased TSH due to release of hormones as a part of inflammation.
After this , phase of hypothyroidism takes place and later on recovery.
Symptoms
Fever for more than 2 weeks.
Throat , or neck pain.
Sore throat with pain referred to ear.
Subacute thyroiditis may also be seen after postpartum – seen after delivery and is not associated with pain, also called silent thyroiditis.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
It is an autoimmune disease often associated with Type 1 Diabetes mellitus, Addison’s disease.
Seen in middle aged females, commonly 45 to 65 years.
CD8+ Tcell cytotoxicity, and antibody development takes place, leading to thyroid gland damage.
SYMPTOMS OF HYPOTHYROIDISM
- Feeling tiredness, weakness
- Dry skin
- Feeling cold
- · Hair loss
- ·Difficulty concentrating
- Poor memory
- · Constipation
- · Weight gain with poor appetite
- · Hoarse voice
- · Irregular menstrual cycle Impaired hearing
- Puffy face , hands and feet ( myxoedema)
MANAGEMENT OF HYPOTHYROIDISM
L- Thyroxine 1.6-1.8 mcg/kg/day is taken on empty stomach at 7 AM in morning.
Breakfast can be taken 30 min later.
Dose needs to be increased in case of Pregnancy, GI disorders, when taking drugs like Rifampicin and Phenytoin.
If you have any questions or you want to tell your story/views, kindly share in comments.
You can also contact our team at halleysclinic@gmail.com
ALSO READ HOW DO YOU KNOW IF YOU HAVE DIABETES?
ALSO READ HOW TO KEEP HEART HEALTHY?








1 thought on “DO I HAVE HYPOTHYROIDISM?”