HOW DO YOU KNOW IF YOU HAVE DIABETES?
- BY DR. AK RANA
Diabetes is a Greek work meaning siphon – to pass through, and and has been known since old times.
Non-communicable diseases like Diabetes have become so much common in population that it no longer looks like a big thing.
Although, with advancement in medical science, there is nothing to be afraid of; still they do affect the quality of our life to great extent. It’s required to be screened on regular basis to avoid it or to treat it at an early stage, so that the major problems like organ damage that follows it and become the cause of morbidity, do not come our way.
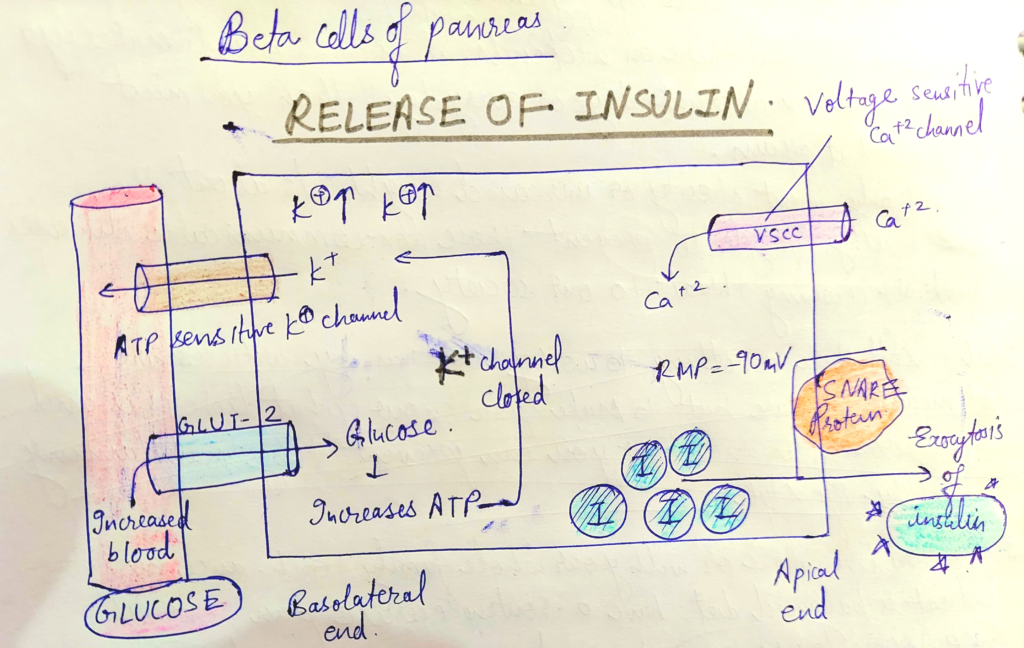
INSULIN, GLUCOSE, & DIABETES
Increase in blood glucose leads to insulin release and that leads to decrease in blood glucose levels (insulin enable cells taking up the glucose from the blood). Insulin is released from beta cells of islets of langerhans in the pancreas, its defect leads to diabetes.
DIABETES AND PANCREAS
TYPES OF DIBETES
[Diabetes mellitus (DM)]
Type 1 – Auto-immune association (destruction of beta cells)
Occurs usually in age group 10-20 years
Type 2 – Insulin resistance
Occurs usually in age group 40-50 years
CRITERIA TO DIAGNOSE DIABETES
- Fasting plasma glucose more than 126 mg/dl
2. 2hr Post Prandial Plasma glucose more than 200 mg/dl
3. Random blood sugar (RBS) more than 200 mg/dl with symptoms
4. HbA1c more than 6.5%
RISK FACTORS
- Centripetal obesity – waist circumference >102 cm in males, >88 cm in females
>90 cm in males, >80cm in females (in Asians)
It causes insulin resistance; cells do not take up glucose leading to increase in blood glucose.
[Obesity leads to lipolysis, formation of triglycerides which are converted to FFA (free fatty acids) that are substrate for new glucose formation and insulin resistance)]
- High- fat diet
- Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity.
- Family history of diabetes or autoimmune diseases.
Why increase in blood glucose such a major concern?
It is because this glucose leads to defective metabolism of carbohydrate, protein; damage liver, kidney and our major blood vessels, that further leads to complications
2. Symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia.
- Increased tiredness
- Increase in chance of infection ( due to defective protein metabolism like
Rhinocerebral mucormycosis
Malignant otitis externa – presents with earache at night.
- Edema
Due to glycosuria( excretion of glucose in urine) there is increased uptake of salt and water in kidney)
3. Diabetic ketoacidosis – patient presents with vomiting, tachycardia, abdominal pain, difficulty in breathing. ( emergency condition)
4. Urinary tract infection
5. Hypertension
6. Atherosclerosis
7. Retinopathy- can lead to vision loss
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES MELLITUS
PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
Insulin –
Rapid acting: Aspart, Lispro, Glulisine
Intermediate acting: NPH
Long acting: Detemir, Glargine
- Biguanides- Metformin
- SGLT-2 inhibitors – Dapagliflozin
- GLP-1 receptor agonists- Liraglutide
- DPP-4 inhibitors
NON- PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
- Carbohydrate content should be 50-60% of total calorie intake.
- Fiber intake should be around 25-40 g per day.
- Protein intake should be 15% of total calorie intake.
- Fat intake should be limited to less than 30%
- Non vegetarians should consume 100-200g of fish/week (rich source of PUFA)
- Vegetarians should consume vegetable oils ( soyabean/ safflower/ sunflower), walnuts and flaxseeds.
- Salt consumption should be less than 5g per day.
- Patients should be advised to avoid smoking, alcohol intake, sugars and sweetened beverages.
PREVENTION OF DIABETES
- A minimum of 150 min/week of physical activity is required. This should involve –
- ≥ 30 min of moderate- intensity aerobic activity each day.
- 15-30 min of work-related activity.
- 15 min of muscle-strengthening exercises ( at least 3 times/week )
- To maintain a good sleep-wake cycle. It keeps our body in rhythm, maintains basal metabolic rate and prevents hormonal changes.
As you see, in our body one key is linked to another and the chain continues.
- In such a busy life, full of stress, time should be or I will say must be taken out to relieve stress by following your hobby, talking to friends and family, taking a walk under wide sky, listening to good music or joining yoga classes.
- Not only in adults, but obesity and lack of physical activity in children also, can create a risk factor for diabetes. They should be given more of outdoor activities daily rather than playing games at home.
Besides generating a healthy attitude at young age will stay with stay with them always and doing daily yoga and exercises will become habit over the time.
Food as I stated before plays a vital role. These days due to busy schedule and not finding enough time to cook or to eat a decent meal (balanced diet); people go towards high glycemic, high fat easy and fast food.
Sometimes here and there, or on weekends, it is fine but if it makes up for your meal on alternate days or every day, then you must think about it again.
It’s not only about obesity or increased weight, it’s about the healthy lifestyle to prevent those non-communicable diseases that are becoming threat to our society.
Either you live alone or with your whole family, each and everyone should eat balanced diet, have a routine exercise plan, enough sleep, and some leisure time to avoid excessive stress and lead a healthy life style.








5 thoughts on “HOW DO YOU KNOW IF YOU HAVE DIABETES?”