HOW DO WE SLEEP?
Always remember, giving enough time to our body to rest is key to rejuvenate our self, feeling fully recharged for the next day.
- BY DR. AK RANA
Sleep is our resting period out of our hectic, busy life. All the animals and birds also sleep, to wake up early in the morning when the first sun ray touches the ground.
To think of a scenario when humans would not require sleep is difficult; even then let’s make an assumption that we don’t need to sleep every day still then at least one day in a week we would need to hibernate for whole day on our Sundays!
But this is not the case, and every day we need a sound sleep of 7.5-8 hours.
Light sleepers require <8 hours
Heavy sleepers require >8 hours
MECHANISM OF SLEEP
Now the main topic, how exactly do we sleep, what exactly this sleep is! For this you must understand that various parts of our brain, hormones, neurotransmitters etc work together to make us sleep.
- Hypothalamus – sleep center – ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPON)
- Pineal gland – melatonin induces sleep
- Cholinergic neurons in pons and midbrain
Neurotransmitter Acetyl choline induces
REM sleep.
NREM-ON neurons via GABA inhibits histamine release from posterior hypothalamus, leading to NREM sleep.
TYPES OF SLEEP
- REM sleep – active sleep/ desynchronized sleep
- NREM sleep – includes N1, N2 and N3 sleep.
Contribution of each stage of sleep
N1- 5%
N2- 45%
N3- 25%
REM- 25%
Dreaming occurs in both REM and NREM sleep
REM sleep – Dreams occur in early morning. They are of long duration. Emotional component is attached to it. They are not related to day to day activities.
NREM sleep – Dreams are of short duration, conceptual and related to day to day activities.
CYCLE OF SLEEP
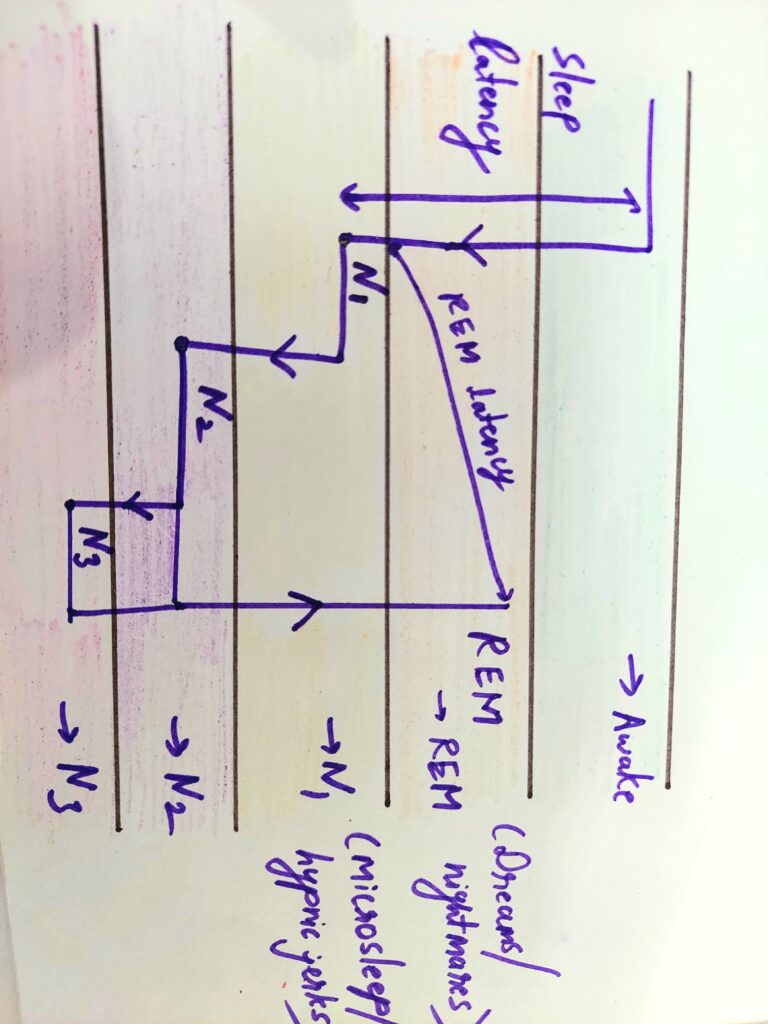
sleep cycle
N3 stage is deepest stage of sleep. It is restorative sleep. The more time we spend in this stage, the more active and energetic we feel the next day.
But, N3 stage decreases with age and hence the quality of sleep also.
WAVES OF SLEEP
Alpha waves – 7 to 14 cycles/second
Beta waves – >14 cycles/second
Theta waves – 4-7 cycles/second
Delta waves – <4 cycles/second
Gamma waves – >60 cycles/second
When we are awake, working on something, talking, watching a movie at that time Beta waves are seen in frontocentral areas along with Alpha waves in occipital area of brain.
While we are meditating (by closing our eyes and focusing) Alpha waves increases all over the brain.
N3 stage/ deeper sleep – Delta waves are prominent.
In REM sleep – saw tooth appearance of waves are seen.
At the time, when we are focused on something with full attention, when brain is most active- Gamma waves are seen.
Do you know there are various chemicals that promote sleep?
It includes- Melatonin, Adenosine, GABA, Galanin
When someone is tired and lethargic, adenosine accumulates in basal forebrain area which leads to sleep.
Caffeine (Tea, coffee, energy drinks) blocks the adenosine receptors and prevents us from sleeping (promote wakefulness).
In a nutshell, when you go to bed and close your eyes you are still awake, and sometimes thoughts make you wonder around, after that you enter REM sleep, where most of our dreams and nightmares exist; for example if you have an exam next day, you will be stressed and in fear and your dream will be based on this component. Next are the short N1 stage and then the long N2 stage. Our quality of sleep depends on the amount spent in deep sleep N3 stage, thereafter comes again the REM sleep where our brain is most active. Although the cycle need not follow the same sequence every time but it’s typically the same 1 and ½ hour cycle. If you are sleeping for 6 hours you are completing 4 such cycles.
You must have noticed sometimes you feel tired and sleepy after you wake up; this is because you woke up in between the cycle of sleep!
INSOMNIA
It is the most common sleep disorder.
It is diagnosed when ≥ 3 months of symptoms are present with significant decrease in quantity and quality of sleep and affecting daily functioning.
Causes
Conditions like Depression, mood disorders, anxiety, chronic medical conditions.
Pharmacological management
- Benzodiazepines – Alprazolam, Clonazepam
They have abuse potential; can lead to dependence if used for longer time.
- Z class drugs- Zolpidem, Zaleplon
- Melatonin
- DORAs – Dual acting orexin receptor antagonists.
- Antipsychotics – Quetiapine
- Antidepressants – Mirtazapine, TCAs
NON PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
- Daily exercises should be included in the routine, can range from moderate aerobic exercises to walking in the park. These can be combined with yoga and breathing exercises.
It helps to purify the body by releasing the toxins. Routine exercises increase the health of all our organs and helps in hormonal balance. It is a mode of tuning the body in shape; you will feel light and your mind will become calm and relaxed.
- Maintain a sleep-wake cycle. You should have a fixed time of sleeping at night.
Various chemicals, hormones, neurotransmitters regulate our sleep, as simple it looks, as complex it is.
At a fixed time body will induce sleep and you should be ready with all your work done, to go to bed.
Taking a short nap in afternoon is beneficial to the body, but just falling asleep at any time is not.
- Sometimes we are in the middle of deciding, planning our work, it’s better to start wrapping up before going to bed and avoid taking it to bed.
All the worries should be written, sorted, updated or cleared, it’s never right to keep thinking about it while you are trying to sleep, because one thing is clear, to sleep your mind should be calm and relaxed.
You should avoid taking late night tea, coffee. At least 1 hour before, you should stop looking at the screen of mobile or laptop as the blue light hamper our sleep.
- When you go to bed and the time you sleep is normally 20min. If it is more than 40 min it is considered abnormal. If it happens, then take a stroll on terrace, drink a little water, clear your mind of ongoing thoughts and then go back to sleep.
Write down your worries for tomorrow, so at least now for next 6-8 hours nothing is worrying you. Your mind should be in no thought -zone for you to sleep soundly.
- The most common mistake that we often commit is thinking about how we are going to fall asleep, now if you are going to divert your brain to that direction, that’s not going to happen.
Always remember, giving enough time to our body to rest is key to rejuvenate our self, feeling fully recharged for the next day.
also read HOW DO YOU KNOW IF YOU ARE ANXIOUS?








4 thoughts on “HOW DO WE SLEEP?”