HOW DO WE SEE COLORS?
- BY DR. AK RANA
Ever played ‘colors game’ in childhood?
Here, group of kids ask the one with the turn ‘which color?’ and he then name one color. Everyone have to run to touch that color, otherwise they are out of the game.
Colors are wonders of life and they never fail to amaze us.
COLORS
Light (visible spectrum of EM waves) travel in straight line.
Light is made up of different wavelengths, each one having its own colour.
For example,
Red colour wavelength = 620- 780 nm
Blue colour = 440 – 490 nm
Green color = 490 – 570 nm
When light strikes an object depending upon its property, object absorbs and reflect other wavelengths.
For example, red dress will absorb all other wavelengths and reflect the red color, this reflected light falls on our eyes and we see it red!
(You can say red dress doesn’t like red colour and just reflected it back, while all others call it as ‘red dress’)
White dress will reflect all wavelengths and black will absorb all.
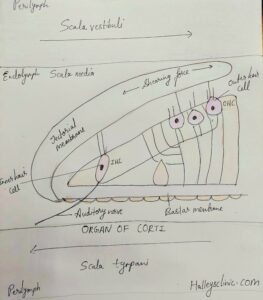
HOW DO WE SEE COLOURS
Our eye has retina and in which photoreceptors are present.
Photoreceptors are of two types –
Rods – associated with vision in dark
Cones – associated with colours.
In case of vitamin A deficiency, rods decrease and thereby decreased vision in night called as night blindness.
Light travels through the cornea, lens and then reaches the retina.
Here cones interpret the colour combination and impulse is generated as passed through optic nerve to optic chiasma to optic tract.
Further ahead it travels to lateral geniculate and to optic radiations and finally in brain to visual cortex.
Anywhere if there is lesion in the pathway, then defect in vision occurs.

halleysclinic.com
COLOUR BLINDNESS
Colour is seen by combination of cones.
The three primary colors are named as –
- Red – Prota
- Green – Deutra
- Blue – Trita
Colour blindness can be acquired or congenital.
Congenital – X-linked recessive inheritance, seen most commonly in males.
(Red and green colour blindness is most common)
Acquired in diseases like – cataract, macular diseases, optic nerve diseases etc.
Dichromatic
Perception of 1 colour is absent, so patient is able to see only 2 colours.
- Protanopia – Red colour blind
- Deuteranopia – Green colour blind
- Tritanopia – Blue colour blind
Trichromatic anomaly
can see all three colours but there is defect in one colour.
- Protanomaly – Red colour defect
- Deuteranomaly – Green colour defect
- Tritanomaly – Blue colour defect
TESTS FOR COLOUR BLINDNESS
- Ishihara chart – most common test
- Hardy Rand Rittler test – for children
- Farnsworth Munsell 100 hue
- Farnsworth Munsell 15 hue
Can you hear your friend talking to you in space?
No way! Because there is no atmosphere and sound waves need vibration of particles for its traveling and reaching our ears.
Can you see your friend in space?
Sure, because light waves do not need medium for traveling.
You can use torch on moon but not radio!
Still, we need source of light.
If you are close to sun or any other star, you will reflect its light and see each other.
But, if there is no source, you won’t be able to see.
We can see moon because of sun, moon reflects sun’s light. The thing is light need to reach our eyes, for us to interpret it.
There are so many shades of single colour, some distinguish them apart, others not so much.
Nevertheless, these colors make our world beautiful and lively.
SHARE YOUR VIEWS AND STORIES IN COMMENT SECTION OR
CONTACT HALLEYS CLINIC TEAM – halleysclinic@gmail.com
also read WHY DO WE FEEL HUNGRY?
also read HOW MEMORY IS STORED IN BRAIN?







1 thought on “HOW DO WE SEE COLORS?”